Conscious Discipline
North College Hill is a Conscious Discipline District
Traditional classroom management systems are based on control. For example, the teacher holds all the power and must control the students. Conscious Discipline is based on connection. It’s a cultural- relationship model that serves our brain’s innately social wiring and utilizes prosocial skills rather than prescribed roles. The power in the classroom is shared in the sense that all parties are responsible for their own behavior. This empowers the teacher as a self-disciplined adult who, in turn, teaches children how to become self-disciplined.
-Excerpt from Conscious Discipline, 2015 by Becky A. Bailey, Ph.D.
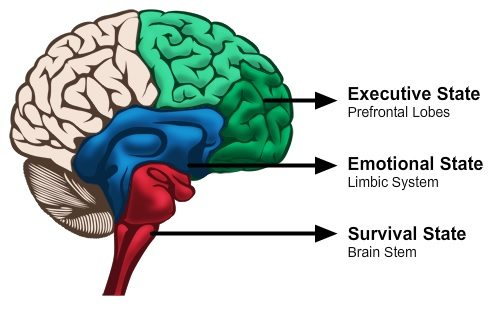
As we learn about Conscious Discipline, we will discover that it is based on brain states: survival, emotional, and executive. Optimal learning occurs when children are functioning in the executive state. We will learn how to identify students’ brain states, regulate our own brain states, and then help children achieve their optimal state.
Conscious Discipline helps educators learn POWERS (perception, attention, unity, free will, acceptance, love, and intention) that help us teach children SKILLS (composure, assertiveness, encouragement, choices, empathy, positive intent, and consequences) using STRUCTURES (e.g., safe places, visual routines, connecting rituals, visual rules, We Care Centers, wishing well, and class meetings).
Over the years working to help students change behavior has resulted in many programs and intervention strategies. Positive Behavior Intervention and Support (PBIS) does not state to use specific practices. PBIS provides a framework for creating intervention plans. Schools adopting Conscious Discipline can use the PBIS framework to ensure systematic decision making and schools adopting PBIS can use Conscious Discipline to meet the PBIS goal of supporting positive behavior in school culture.
Essential Takeaways
- Understanding the adult role in responding to behaviors with children is key.
- Assessing the child’s state and what developmental questions are unanswered begins the intervention plan process.
- When creating a behavior intervention plan, begin with identifying the wanted behaviors.
- In the data collection process, track the wanted behaviors.
Four Components of Conscious Discipline
Conscious Discipline is an evidence-based, trauma-informed approach. It is recognized by the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration’s (SAMHSA’s) National Registry of Evidence-based Programs and Practices (NREPP), and received high ratings in 8 of 10 categories in a Harvard analysis of the nation’s top 25 social-emotional learning programs. The Harvard study’s authors say, “Conscious Discipline provides an array of behavior management strategies and classroom structures that teachers can use to turn everyday situations into learning opportunities.”
Conscious Discipline encompasses these four components, which are scientifically and practically designed for success:

How Does Conscious Discipline Compare
Ten Reasons to Shift to Conscious Discipline

For more information about Conscious Discipline > Click Here
